Cyprus’ energy challenges are set to intensify in 2026, as experts warn that unresolved issues from the current year will continue to affect the sector. Persistent high electricity prices and potential rolling power cuts loom large on the horizon.
- With so many unresolved issues, stakeholders are urged to take swift action to ensure a more sustainable energy future for Cyprus.
Energy challenges: Urgent Decisions Required
According to Constantinos Hadjistassou, a professor at the University of Nicosia who specialises in energy, the leeway for errors in Cyprus’ energy decision-making is critically low. He emphasised the need for increased coordination among policymakers and experts to address the pressing challenges ahead.
High Electricity Prices
Energy expert Charles Ellinas echoed Hadjistassou’s sentiments, stating that the energy sector remains one of Cyprus’ most problematic areas. Despite some successes in 2025, the lack of tangible results necessitates urgent attention to the high cost of electricity, which is not expected to decrease in 2026.
Ellinas highlighted that Cyprus has the highest per capita carbon dioxide emissions in Europe, primarily due to its reliance on diesel and heavy fuel oil for electricity generation. He stressed the urgent need to transition to natural gas to mitigate these emissions.
Challenges with LNG and Natural Gas
The LNG import project at Vasiliko continues to face difficulties, with experts noting that the completion of the pier construction is straightforward from an engineering perspective. However, the lack of a clear plan or timetable hampers progress. If completed, the project could allow Cyprus to benefit from lower LNG prices expected in 2026.
Energean has proposed supplying natural gas through a submarine pipeline from its fields in Israel, contingent on the opening of Cyprus’ natural gas market. Hadjistassou pointed out that the energy ministry has several options available for early 2026, but delays in transitioning from diesel to natural gas will burden Cypriots with high electricity prices.
Offshore Gas Exploration Prospects
Looking ahead, the development of the Kronos gas field is anticipated to proceed quickly, with exports to Egypt expected by early 2028. However, Ellinas cautioned that while this may yield political advantages, it will not significantly enrich Cyprus, with profit shares expected to be less than 0.7 per cent of the annual budget.
The progress of the Aphrodite gas field remains uncertain. Despite the resolution of disputes with Israel, Chevron must decide on investments in 2026 to move forward. With a focus on high-yield projects, Chevron’s low capital expenditure plan complicates progress on the Aphrodite project, which is estimated to cost $4 billion.
International Collaborations and Infrastructure Projects
The EEZ delimitation agreement with Lebanon, although politically significant, is not expected to yield direct benefits. Hadjistassou noted that Chevron is prioritising other projects, such as gas agreements with Egypt, over the Aphrodite field.
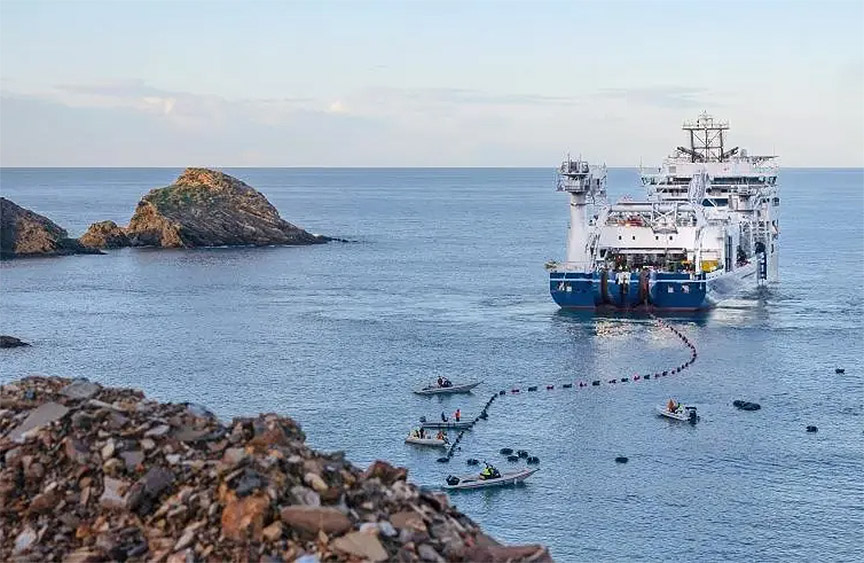
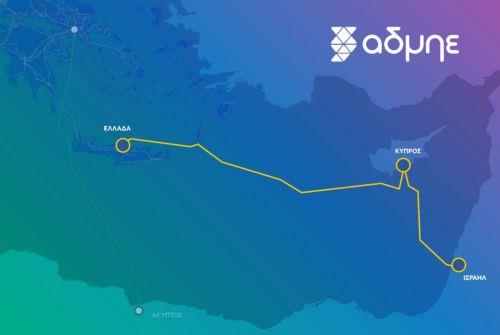
Ellinas mentioned the Great Sea Interconnector, a proposed subsea cable linking Cyprus and Greece, which needs decisive action to become operational by the planned 2030-2031 date. The project has received backing from the European Commission and Greece, fostering hope for its advancement despite ongoing governmental ambivalence.
Recent Developments in the Interconnector Project
The trilateral agreement between Cyprus, Greece, and Israel on December 22 aims to promote the Great Sea Interconnector, linking it to the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC). Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu underscored the significance of this collaboration, highlighting its potential to enhance energy connectivity between Europe, Asia, and the Arabian Peninsula.
Despite the commitment, Hadjistassou referred to the project as the “not-so-Great Sea Interconnector” due to lingering uncertainties about its viability and investor interest. The financial burden of the project will largely fall on Cypriot taxpayers, raising concerns about the effective use of funds.
Renewable Energy Integration Challenges
As Cyprus grapples with its energy transition, integrating renewables into the grid remains a pressing issue. Hadjistassou warned that power cuts are likely to increase in 2026, particularly during periods of low electricity demand when the generation from renewable sources peaks. Without adequate battery storage, a significant portion of this generated electricity could go to waste.
He suggested that a portion of the surplus electricity could be redirected to desalination plants to combat water scarcity, highlighting the need for innovative solutions to manage excess electricity.
The Future of Electricity Supply
Another critical concern for 2026 will be ensuring a stable electricity supply on the island. With the increasing reliance on renewable energy, the Dhekelia power plant’s role in maintaining grid stability is becoming more crucial. Although the Electricity Authority of Cyprus (EAC) plans to install gas turbines to enhance capacity, they will not be operational until 2028.
In the meantime, the EAC expects to have a 160MWh battery bank at Dhekelia operational by summer 2026, which could help alleviate power cut issues. Additionally, the Transmission System Operator (TSO) aims to install another 400MWh of battery storage systems by mid-2026, further bolstering the island’s energy resilience.
Looking Ahead
Despite these initiatives, the cost of stored electricity will be higher than that generated from conventional sources and renewables, posing another challenge for consumers. As Ellinas summarised, 2026 is set to be another year of significant energy challenges for Cyprus, with urgent priorities including completing the LNG import project, enhancing electricity storage, upgrading the grid, increasing renewable energy installations, and deciding on the Great Sea Interconnector.
With so many unresolved issues, stakeholders are urged to take swift action to ensure a more sustainable energy future for Cyprus.